Connecting and authenticating with the Explorer
The Explorer automatically attempts to connect to your GraphQL server at the URL specified in its Settings tab.
When you use the Explorer with a cloud supergraph, the endpoint URL is always the URL of your current variant's GraphOS-managed router.
Depending on your GraphQL server's settings, you might need to configure the Explorer's connection to handle CORS requirements or authentication.
CORS policies
Requests from the Explorer go straight from your browser to your GraphQL server, so your endpoint sees requests coming from this domain: https://studio.apollographql.com
It's common for public endpoints to set CORS policies that restrict which domains can query them. If your endpoint has CORS protections enabled, you probably need to safelist https://studio.apollographql.com in your CORS policy to use the Explorer.
To do so, include the following header(s) in your server's responses:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://studio.apollographql.com# Include this only if your server *also* authenticates via cookies.Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
If you can't change your CORS policy, you might be able to create a proxy for your endpoint and point the Explorer to the proxy instead. CORS policies are enforced by browsers, and the proxy won't have the same issues communicating with your endpoint.
Authentication
The Explorer provides features to help you authenticate via request headers, cookies, and scripts.
If your graph has authentication requirements that aren't covered by these options, please contact support@apollographql.com with questions or feedback.
Request headers
The bottom panel of the Explorer includes a Headers tab where you can set headers that are included in your operation's HTTP request.
Headers can include the values of environment variables, which are injected using double curly braces as shown:
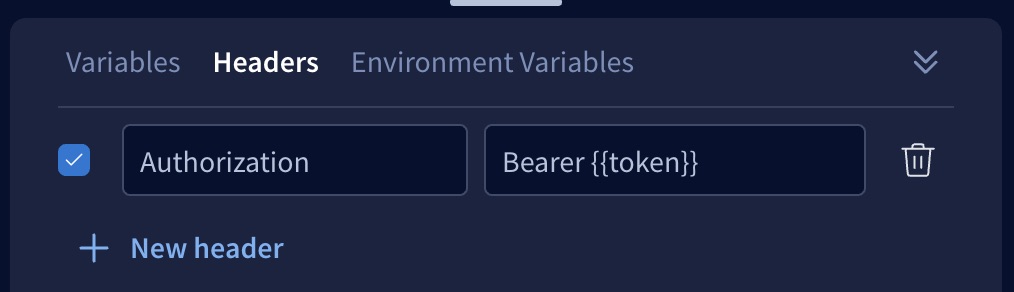
Cookies
If your server uses cookies to authenticate, you can configure your endpoint to share those cookies with https://studio.apollographql.com
To set this up, your cookie's value must contain SameSite=None; Secure. Additionally, the following CORS headers must be present in your server's response to Studio:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://studio.apollographql.comAccess-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
Once configured, requests sent from https://studio.apollographql.com include the cookies from your domain when you run queries with the Explorer. If you're logged in on your domain, requests from the Explorer will also be logged in. If you log out on your domain and the cookie is removed, requests from the Explorer will be logged out.
Environment variables
The Explorer's Settings tab includes a section for defining environment variables. Here, you can provide sensitive information that you can then inject into header values, GraphQL variables, or scripts. This enables you to share operations (including their headers) with other team members without exposing this sensitive data.
Defining
You define environment variables in the Explorer's Settings tab, like so:
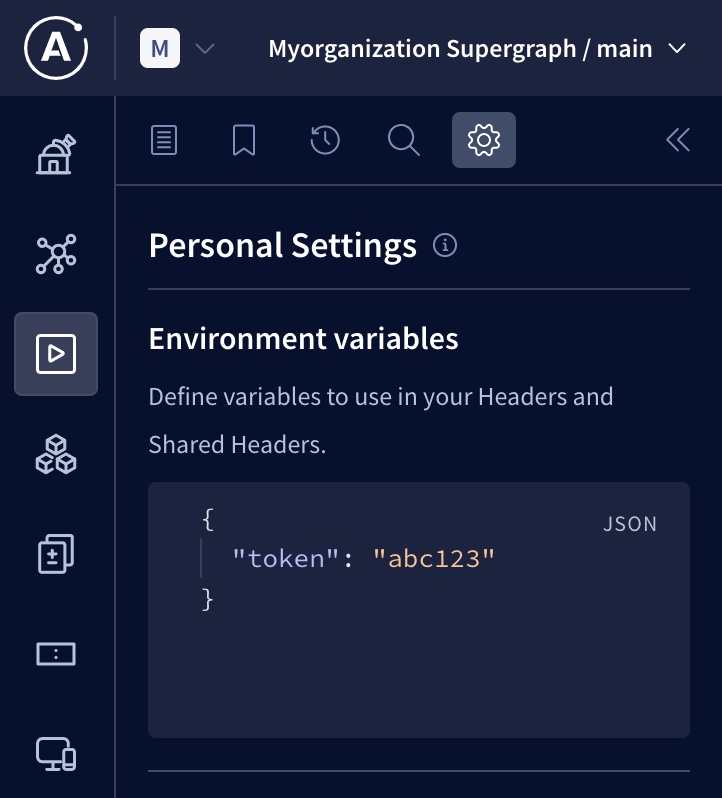
If you share an operation that uses environment variables with your team members, your values for those environment variables are not shared, and other users can provide their own values.
Injecting
You can inject your Explorer environment variables into any of the following:
Header values
Inject an environment variable into an HTTP header value by surrounding the variable's name with double curly braces, as shown:
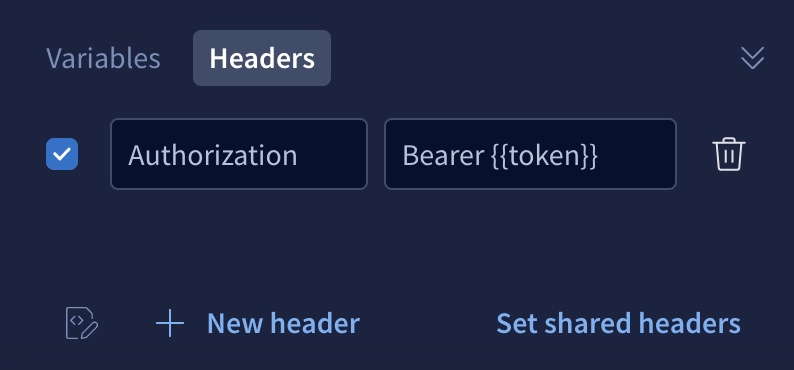
GraphQL variables
Inject an environment variable into a GraphQL variable value by surrounding the variable's name with double curly braces, as shown:

Custom scripts
If you create a custom script that runs before an operation executes, that script can access an environment variable's value like so:
const secretToken = explorer.environment.get('token');
Scripting
Similar to tools like Postman, the Explorer can run custom scripts when executing each GraphQL operation. These JavaScript-based scripts often populate the values of environment variables that are then injected into HTTP header values or GraphQL variables. This can be especially useful for managing authentication flows like OAuth, for example by refreshing an expired access token, or validating response data. For an example, see Operation Scripts.
Script types
You can define two different types of scripts:
- Preflight scripts. You can define a single preflight script per variant of a graph. This script runs before every Explorer operation that's executed against the associated variant (unless a user individually disables the script).
- Preflight scripts are especially helpful for enabling organization-wide Explorer authentication against your graph.
- Operation scripts. If you use operation collections, you can define a separate script for each saved operation in a collection. This script can then control everything that happens before, during, and after an operation is executed (as long as a user individually enables the script).
- Operation scripts are especially helpful for debugging the behavior of individual operations when they're provided various values.
If an Explorer operation runs both types of scripts, the preflight script runs before the operation script.
Important considerations for Explorer scripts
- Scripts are stored in the Apollo cloud in plaintext.
- Do not include secret credentials in scripts! Instead, team members can provide their individual credentials to the Explorer via environment variables.
- If a team member has view access to a particular graph variant or operation collection, that team member can also view any scripts associated with that variant/collection.
- Preflight scripts are enabled by default, and individual team members can disable them.
- Operation scripts are disabled by default, and individual team members can enable them.
Preflight scripts
Creating preflight scripts
For protected variants, only organization members with the Graph Admin role can create or edit a variant's preflight script.
For non-protected variants, members with the Contributor role can also modify the preflight script.
To create a preflight script:
Open GraphOS Studio and then open the Explorer for the graph and variant you want to create a script for.
Open the Explorer's Settings tab and scroll down to the Preflight script section:

Click Add script. The following dialog appears:
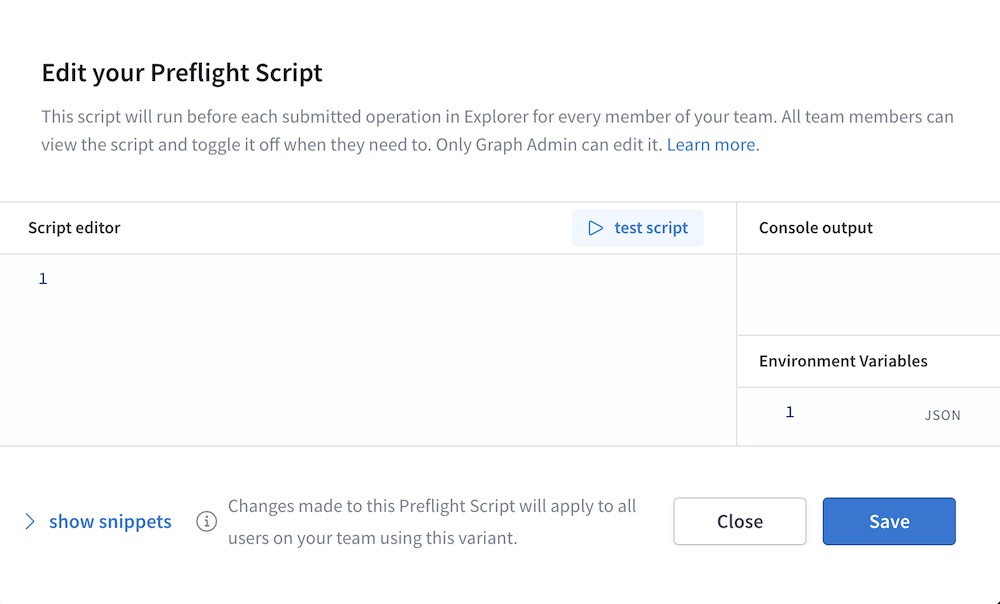
Click Show snippets to display a list of common helpful actions you can perform from your preflight script (such as sending HTTP requests and interacting with Explorer environment variables).
Develop your script in the Script editor panel. As you develop, you can click Test script to test its execution. Console messages are printed in the Console output panel.
When your script is ready, click Save. Studio stores your script.
You're done! After you save your script, it's automatically loaded for any team member that uses the Explorer with the associated variant.
Disabling preflight scripts
By default, a variant's preflight script runs automatically before every GraphQL operation that's executed in the Explorer. Team members can individually disable the script from the Personal Settings > Scripts section of the Explorer's Settings tab:
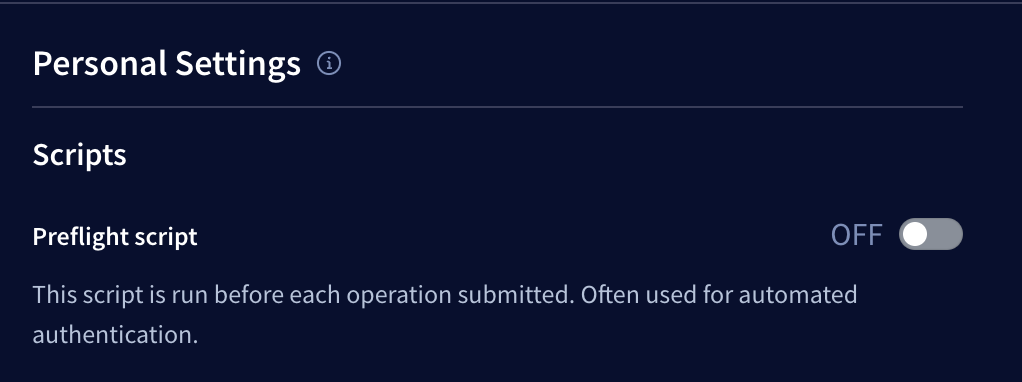
To do so, toggle the switch to OFF.
Operation scripts
Creating operation scripts
You can only create operation scripts for operations that are saved in an operation collection.
Only organization members with edit access to a particular operation collection can create or edit operation scripts for that collection.
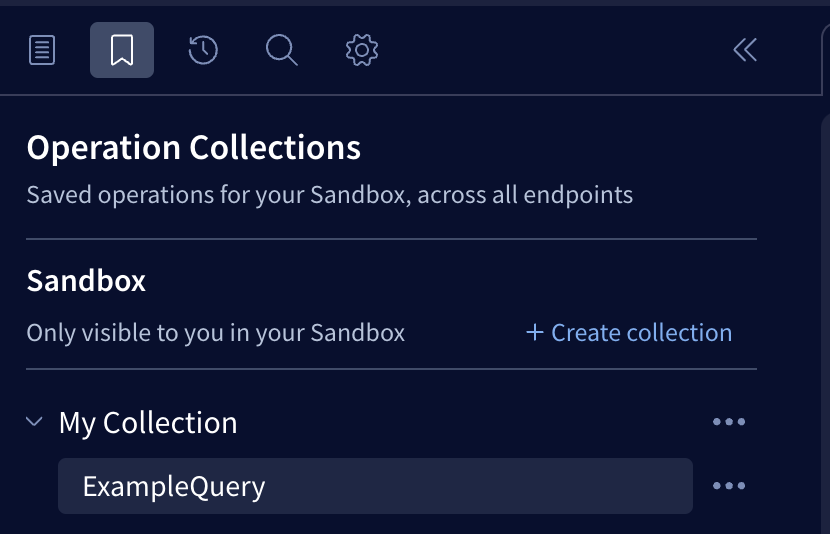
From the Explorer, open an operation from the Operation Collections menu:
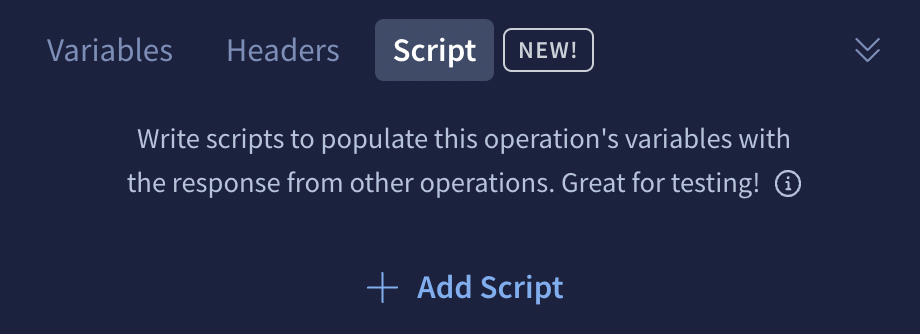
From the Explorer's bottom panel, select the Script tab and click + Add Script:
The following modal appears:
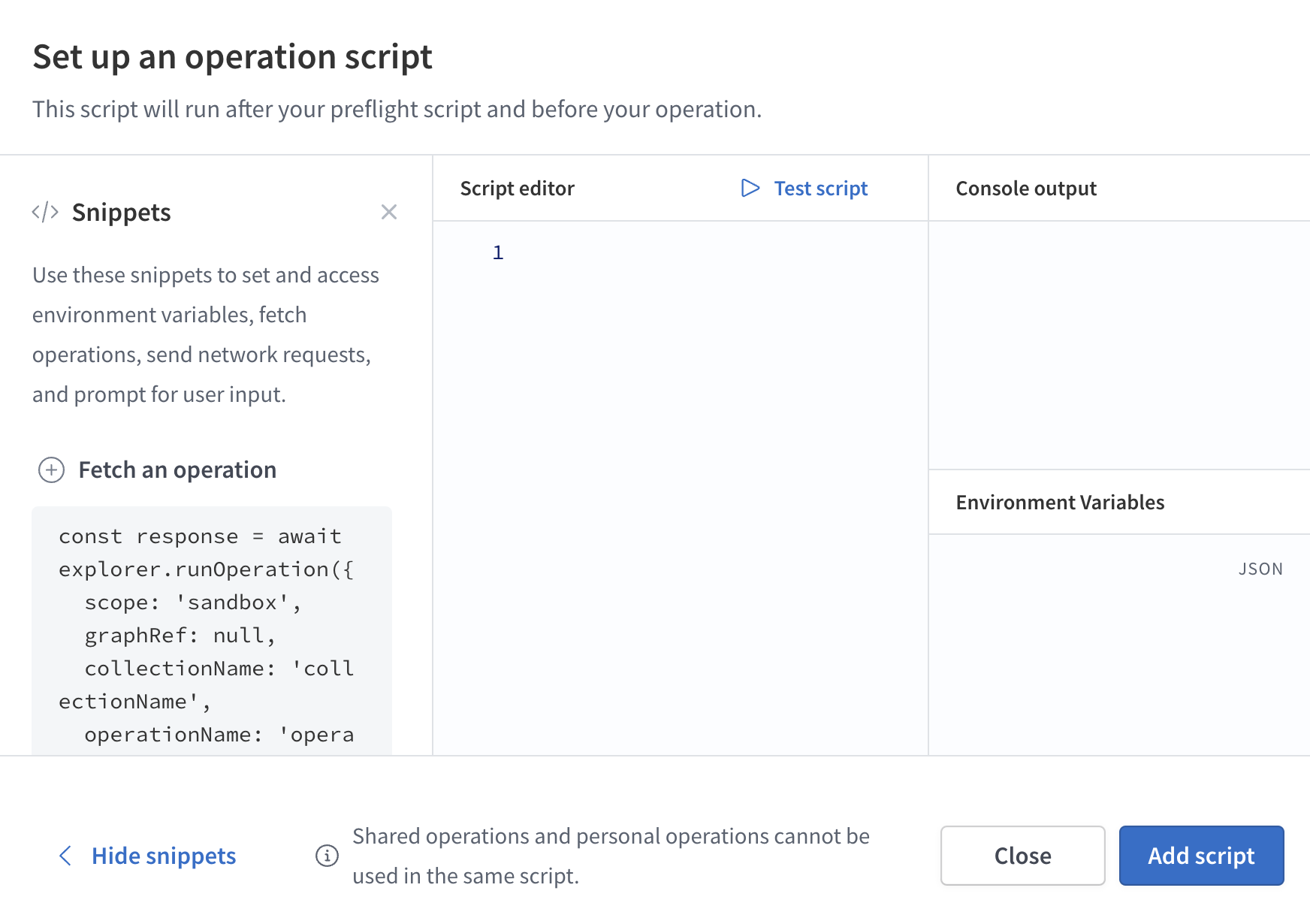
Create, test, and save your script.
- For details on script creation, see Creating preflight scripts.
Enabling operation scripts
By default, operation scripts are disabled for each individual user. Users can enable operation scripts from the Explorer's Settings tab:

Chaining operations
A script can use the explorer.runOperation function to execute another operation that's saved in a collection. That operation might in turn have its own script, which can also call explorer.runOperation.
You can use this mechanism to chain together a sequence of operations for more advanced authentication flows.
Scripting API reference
These symbols are available within the scope of both preflight scripts and operation scripts. Snippets for these symbols are available via the Show snippets link in the scripting dialog.
| Name / Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Function that returns the current value of the environment variable with the specified |
| Function that sets a new value for the environment variable with the specified |
| Function for making HTTP requests to external services from within a script. Network requests are initiated from an origin of |
| Function for executing other saved operations. If the target operation has defined its own script, it will run before its operation.
|
| Function that prompts the user for input and returns the value in a promise. If the user cancels the prompt, the promise resolves to The prompt supports Markdown rendering of the |
| Function that prompts the user to authenticate using your OAuth 2.0 provider's URL (specified by This function returns a promise containing the query parameters from your OAuth provider's response. If the user cancels the prompt, the promise resolves to For OAuth 2.0 authentication to work with the Explorer, your OAuth 2.0 provider must recognize |
| The body of the |
| This exposes the |
Examples
Operation Scripts
Here is a small example that runs an operation and sets an environment variable for use on future operations:
const response = await explorer.runOperation({scope: 'shared',graphRef: 'SpaceX-pxxbxen@current',collectionName: 'Mission Control',operationName: 'Ships',})const firstShipID = response.result.data.ships[0].idexplorer.environment.set('shipID', firstShipID)